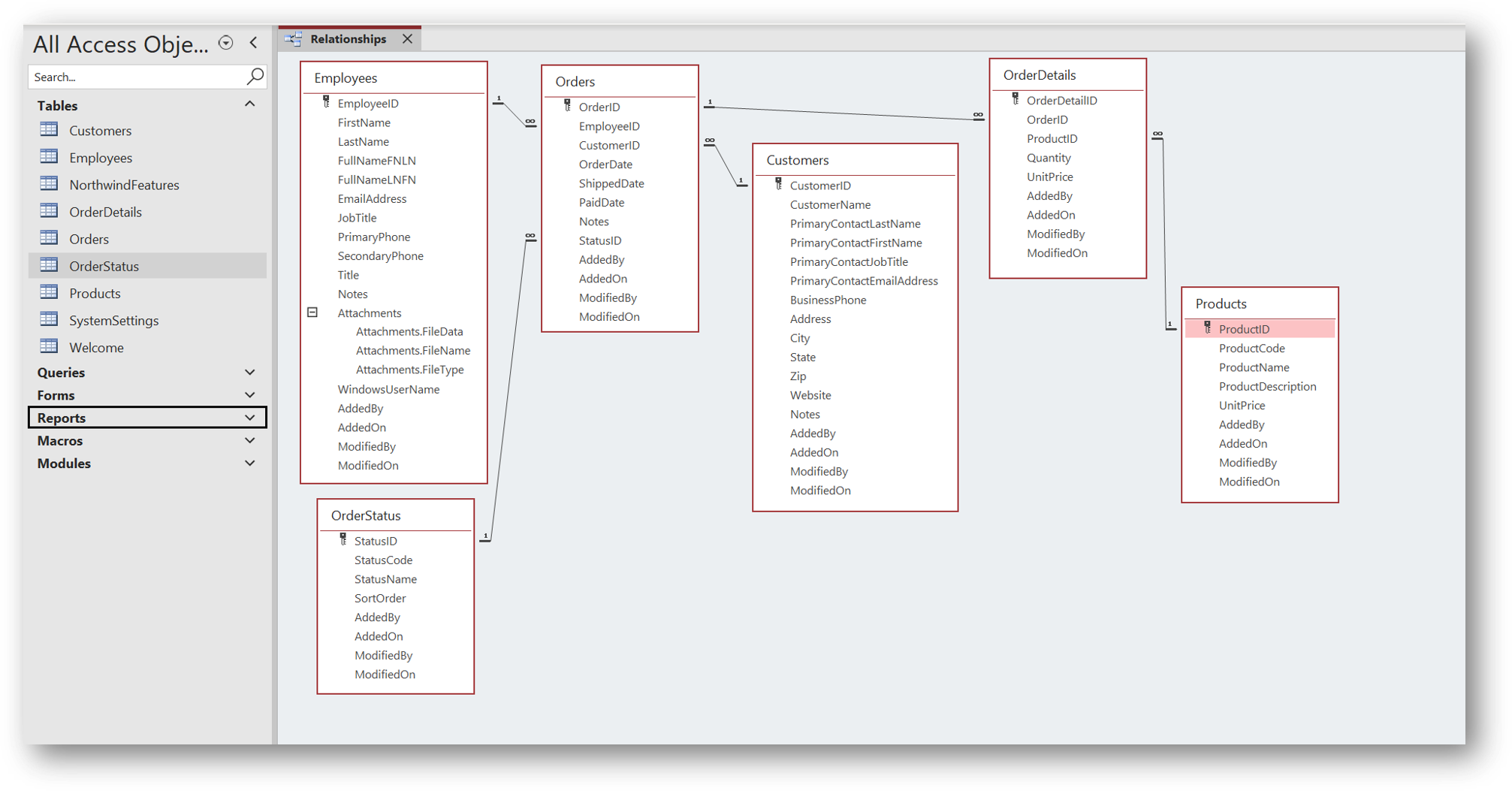
Relational Databases

What are the components of a relational database and
how do they compare with what we already know?
Definitions
a database is a collection of related data
a database management system (or DBMS) is a system designed for two main purposes
- to add, delete, and update data in the database
- to provide various ways to view (on screen or in print) the data in the database
a flat file database
is one where all the data is contained in a single table, such as in Excel
comparing flat file databases to relational databases
a
relational database
is one in which you can store information in different tables,
each containing different information that relates to information in the other tables
... an entity-relationship model (ERM) is an abstract and conceptual representation of data.
Entity-relationship modeling is a database modeling method, used to produce a type of conceptual schema
or semantic data model of a system, often a relational database,
and its requirements in a top-down fashion.
Diagrams created by this process are called entity-relationship diagrams (or ER diagrams)
One has choices in how to model the elements in a database.
One of the standard textbooks on the topic (Elmasri, R., & Navathe, S. (2011).
Fundamentals of database systems. Boston: Addison-Wesley.)
offers a view of the several methods.
The purpose of a database is to store information about certain types of objects.
To make the distinctions clear, we will use a color schema in which we use
terms relevant to entity relationship models
and their correlates in Excel
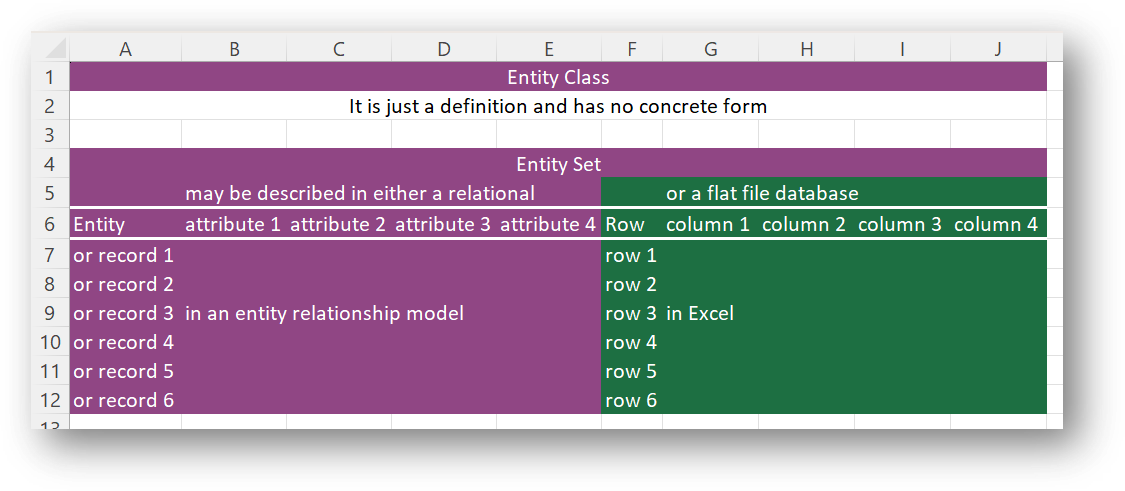
An entity class [like books] is an abstract definition of something
In Excel, there is no correlate as it is just a definition, not an example of a definition
- ERModel entity class
- [there is no correlate in Excel]
- an abstract definition of something
- [there is no correlate in Excel]
- [like "books"]
- [there is no correlate in Excel]
An entity set
is the list of given entities
within a given entity class that are currently in the database
In Excel, an entity set is a worksheet
- ERModel entity set
- Excel worksheets
- composed of entities
- composed of rows
- which have attributes
- which have column cells
an entity
[like a textbook for INLS161] is a concrete example of that description
In Excel, an entity is a row
- a concrete example of that description
- a concrete example of what the table represents
An entity is composed of attributes
in Excel, attributes are columns
attributes/columns include information we want in the database
attributes/columns help to uniquely identify individual entities within a class
attributes/columns can describe relationships between entities in different classes
Primary and Foreign Keys
a Primary Key
is a set of
attributes/column cells
that uniquely identifies an
entity/a row
a Foreign Key
is a copy of the Primary Key
of one entity/row
that appears as
an attribute/column cell
in another entity class/worksheet
and helps define the relationship between
entities/rows
in the two entity classes/worksheets
these keys link together the related entities/rows
in a relational database/entity set