INLS 131-1 University of North Carolina at Chapel
Hill
(c) Anne Parker and UNC-CH
Managing Change
Agenda
October 15, 1996
- An environment for change
- The change process
- Some tools for managing change
Senge: "An organizational culture in which individual development
is a priority, outmoded and erroneous ways of thinking are actively
identified and corrected, and the purpose and vision of the organization
are clearly understood and supported by all its members."
(Worrell)
Garvin: "An organization skilled at creating, acquiring,
and transferring knowledge, and at modifying its behavior to reflect
new knowledge and insights." (Worrell)
Learning Organizations
Five core disciplines
(Senge)
- Personal mastery
Organizations can't learn, only individuals can learn; continue
to see reality more clearly; lifelong process
- Mental models
Frameworks through which individuals see and understand the
world; can limit reasoning, therefore continuously identify (make
explicit) and test mental models.
- Shared vision
Images of what the organization should be -- what the members
are trying to create.
- Team learning
Align and develop the capacity to work as a team; defining
and clarifying roles and responsibilities.
- Systems thinking
Senge's fifth discipline; foundation of theory. Without systems
thinking mgt. has a tendency to look for familiar solutions; use
short term fixes which may shift the problem elsewhere or fail
to fix the underlying problem. Uses systems archetypes to define
most common management situations.
Learning Organizations
Systems Archetype Example
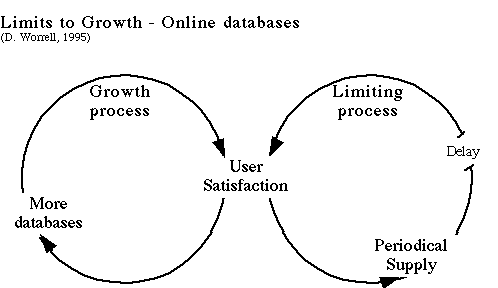
(K. Lewin)
 change -> refreeze">
change -> refreeze">
(Montana and Charnov)
- Scanning activities and/or external events
(can use focus groups as one means of identifying external
events)
- Idea for change
(can use brainstorming)
- Identify the scope of the problem
(validate with focus groups)
- Develop alternatives
(validate, get buy-in, with focus groups)
- Analyze alternatives tempered by constraints
- Select an alternative
(validate, get buy-in, with focus groups)
- Implement change
- Evaluate results
(can gather data with focus groups among other techniques)
(Repeat)
Note: Reality is much less linear -- many feedback loops. No
recognition of need to "unfreeze"
(Adapted from Everett Rogers, Diffusion of Innovations, New York,
Free Press, 1983)
Innovation: "an idea, practice or object that is perceived
as new by an individual or other unit of adoption" (Rogers,
p. 11)
Encouraging Innovation:
Attributes of Innovations
(Except where noted, these attributes of an innovation are positively
associated with earlier adoption of an innovation)
- Relative advantage
- Compatibility
- Complexity (negative association)
- Trialability
- Observability
- Potential for reinvention (flexibility)
- Product vs. process
- Discretionary vs. required use
Encouraging Innovation:
Innovation Adopter Categories
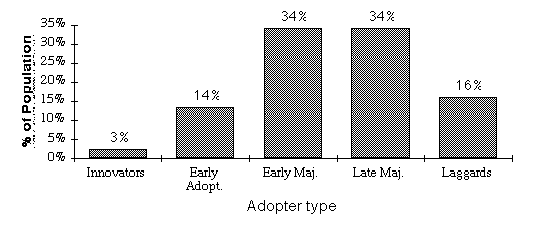
Encouraging Innovation:
Adopter Characteristics
| Category | Characteristics
| Marketing and Support Strategies for Technology Innovations
|
| Innovators | Venturesome, risk takers
Good contacts outside peer groups
Can cope with high uncertainty
Internally motivated
May or may not be respected by peers
| Opportunity
Generally relevant examples
Technical information
|
| Early Adopters | Respectable
More integrated into local social system than innovators
Opinion leaders
Make judicious innovation decisions
Internally motivated
| Opportunity
Domain examples
Critical success factor information
Technical information
Tacit administrative support
|
| Early Majority | Deliberate
Adopt innovations just before average
Follow others in adopting innovations, but seldom lead
Externally motivated
| Incentives + opportunity
Domain examples
Procedural training
Central technical support
Administrative support
|
| Late Majority | Skeptical
Adopt slightly later than average
Adopt for economic or peer pressure reasons, not usefulness
Unwilling to risk scarce resources
Externally motivated
| Incentives + "push"
Specific peer examples
Technical and pedagogical training
Local support
Admin. encouragement
|
| Laggards | Traditional
Last group to adopt
Have almost no opinion leadership
Point of reference is the past
Have limited resources, unwilling to risk
| Incentives + "push"
Specific peer examples
Technical and pedagogical training
Peer mentoring
Admin. encouragement
|
- Application: Problem definition; solution evaluation
- Direct inquiry with groups of "customers"
- Representative sample:
Large group, highly structured topic
vs.
Small group, unstructured topic
- Limit questions
- Open-ended data collection
- Neutral questioning
- Check behavioral intentions
Tools for Managing Change
Analyzing focus group data
| Customer words | Product/ Service Requirement
| Who | How
| Where | Possible quality indicators
| Possible features |
| . | . | . |
. | . | . | .
|
| . | . | . |
. | . | . | .
|
- Agree on question
- Write it down
- Review guidelines:
- No evaluation, criticism, or discussion
- Creativity/ wild ideas welcome
- Hitchhike -- build on each others' ideas
- Record every idea; use originator's own words
- Work quickly
- List ideas (Structured or unstructured)
- Clarify list: eliminate duplicates
- Proceed with prioritization/ decision method
(Penny Matrix variation)
- Decide who will rate
- Assign each rater a number of pennies to spend
- Have raters spend their "money"
- Total the expenditures for each item
Return to Course
Outline


 change -> refreeze">
change -> refreeze">
