Institutional Records Management
Week 06 (2/19)
INLS 525
Myburgh (2005)
- She states "Archives are political." What does she mean?
- What then is Records Management?
Recordkeeping systems are business information systems capable of: capturing, maintaining, and providing access to records over time.
Recordkeeping systems are not simply software applications designed to manage records. They are an organised collections of: people, policies, procedures, tools, technology, ongoing supporting education, and maintenance. In combination, these combinations enable organisational business to be adequately documented.
Emphasis added.
See also: ISO 15489
Traditional Records Lifecycle
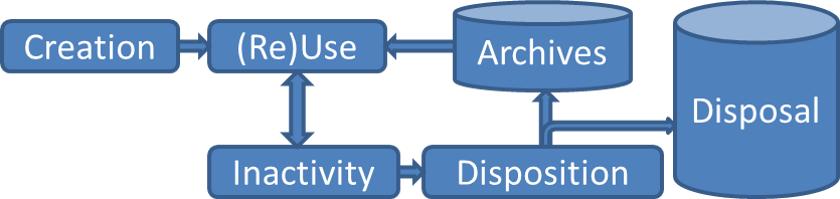
- Who is responsible for what portions of the traditional lifecycle?
- How is the continum model different?
According to DIRKS: what is the primary difference between Business Information & Recordkeeping Systems?
Appraisal
What should we keep, how long, and why?
- Frequently identified as most important ARM function
- Identification of the few (1-5%) records worth preserving, i.e. those with continuing value
- Largely a result of records volume explosion in mid-20th century
- Shift from collector to selector role (reduction of bulk)
Stephens & Wallace on Appraisal
Identifing the Primary & Secondary values
- Administrative or opperational
- Research or historical
- Legal
A records series can (and usually does) possess several of these values simultaneously, and they may change. (pg 46)
See also Cost/Risk/Benefit & Retention Options.
Electronic Document & Records Management Systems
(EDRMS)
Document Management
- Check-in and check-out
- Version control
- Document review and approval
Records Management
- Metadata management
- Classification
- Archives and disposal
- Management of physical records
See Joseph, Pauline. "EDRMS 101: The Basics." Information and Records Management Annual 25 (2008): 9–26.
14 Principles of ER Retention
- How does Stephens & Wallace define an Electronic Records Series?
- How are retention periods identified?
- What aspects of records do Systems Developers & End Users provide?
- How applicable are Stephens' recommendations 12 years later?
Retention Scheduling
- For active/semi-active records
- Retention schedule elements
- Series label
- Description
- Retention Period
- Disposition Action
- Legal or other authority
- Two main types of schedules: general & specific
- Traditionally based on series, but often now based instead on systems or functions
Holds - Suspension of Disposition Actions
- When receiving notice or having reasonable anticipation of litigation, must cease normal disposition actions that would destroy related data, e.g.
- Implementing deletion based on retention schedules
- Recycling of backup tapes
- Perhaps even defragmenting hard drive
Evidence
Something (including testimony, documents and tangible objects) that tends to prove or disprove the existence of an alleged fact.
- Black’s Law Dictionary, "Evidence" (7th ed. 1999)
According to Myburgh: how is the concept of Evidence different between Archives & Records Management?
DIRKS
Recordkeeping is the making and maintaining of complete, accurate, reliable evidence of business transactions.
- What are the 6 charactaristics of good recordkeeping systems?
- How do they support good recordkeeping?
Giordano (2004) puts it another way: evidence must also be relevant, authentic, and reliable.
Reliability
- Authority & trustworthiness of a record as evidence
- Records ability to stand for the facts / entity of which it is evidence & treated as that fact in itself (e.g., passport = citizenship)
- Provided by a record’s
- form (e.g., date, signature)
- procedure of creation (signing authority, routing, handling during compilation & completion, filing, etc.)
Duranti, Luciana. "Reliability and Authenticity: The Concepts and Their Implications." Archivaria 39 (1995): 5-10.
Giordano (2004) on Reliability
[C]ourts may have fallen prey to this notion that while errors do occur, most software is reliable for authentication purposes. (170) …
[W]e, as a culture, have taken as an article of faith the reliability of computer technology. (173)
"the fact that it is possible to alter data contained in a computer is plainly insufficient to establish untrustworthiness." United States v. Bonallo, 858 F.2d 1427 (9th Cir. 1988)
(165)
Integrity, Fixity, & Accessibility
I.E. Authenticity
- Hasn’t been subject to undocumented manipulation
- Technological (e.g. checksums, digital signatures) & procedural (e.g. security, monitoring of changes to technology or users’ knowledge base) elements
- Essential characteristics of the record can still be reproduced on current technology
(RFC 3227)
- "Such collection represents a considerable efforts on the part of the System Administrator."
- "Keep detailed notes."
- "Minimise changes to the data as you are collecting it."
- "Do collection first and analysis later."
- "Proceed from the volatile to the less volatile."
- Computer evidence should be: admissible, authentic, complete, reliable, believable
DIRKS
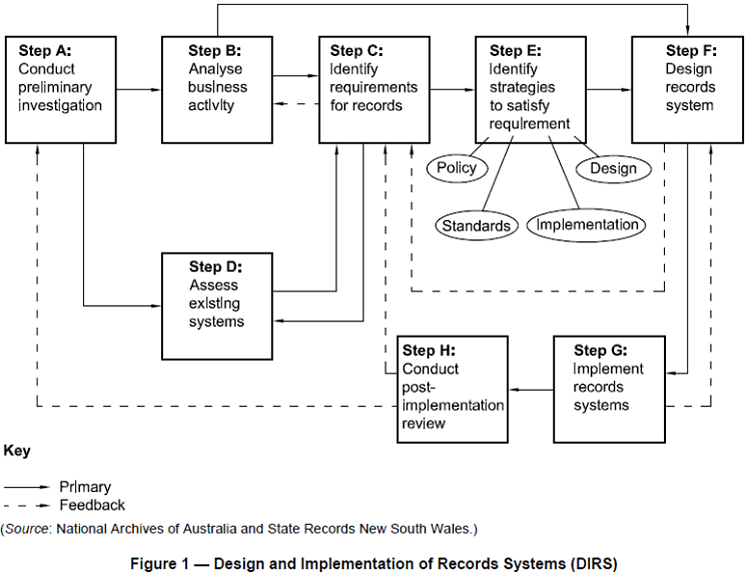
Preliminary Investigation
- "Identify and document the role of your organisation, its structure, the business, regulatory and sociopolitical environments in which it operates, and major factors affecting its recordkeeping practices"
- "Snapshot of your organisation’s business activity and major stakeholders"
- "Identify particular problem or risk areas"
- "Crucial contextual information about factors that influence your organisation’s need to create and maintain records"
To do:
- "determine the scope of the preliminary investigation"
- "collect information from documentary sources and interviews"
- "document your research"
- "prepare a report"
Analysis of Business Activity
"Develop a conceptual model of what your organisation does and how it does it by examining its business activities and processes"
To do:
- "collect information from documentary sources and interviews"
- "analyse the work performed by the organisation"
- "identify and document each business function, activity and transaction"
- "develop a business classification scheme based on a hierarchy of business functions, activities and transactions"
- "validate the analysis of the organisation’s business activity with senior management"
Identification of Requirements
"Identify and record your organisation’s requirements to make and keep evidence of its business activities and to document the requirements in a structured and easily maintainable form"
To do:
- "locate relevant sources"
- "identify regulatory, business and community requirements for recordkeeping"
- "document these identified requirements in a manner suitable for"
- "reference purposes"
- "determine and document which of the identified requirements will be met"
Assessment of Existing Systems
"Survey your organisation’s existing recordkeeping and other information systems to measure the extent to which they provide evidence of business activities, or have the required functionality to do this"
To do:
- "identify existing paper-based, electronic and hybrid business information systems within the organisation"
- "analyse whether your organisation’s prioritised recordkeeping requirements are being met"
- "determine whether current systems have the capacity to meet them (by measuring the 'gap' between 'what you have' and 'what you want')"
- "prepare a report describing the strengths and weaknesses of existing information and records management practices”


